Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It is prevalent worldwide and can affect both men and women. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for gonorrhea is essential for early detection and prevention of potential complications.
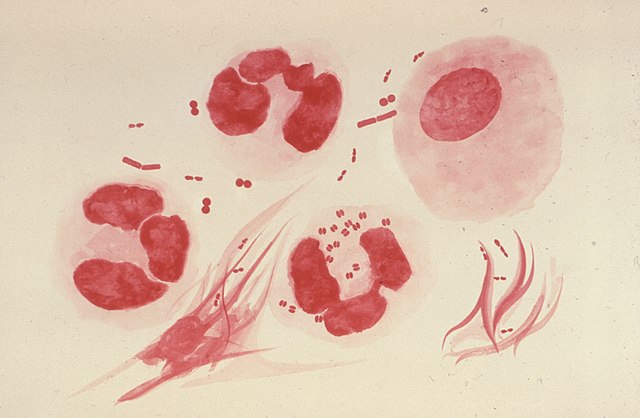
Causes
Gonorrhea is primarily transmitted through unprotected sexual contact with an infected individual. This can include vaginal, anal, or oral sex. The bacterium thrives in warm, moist areas of the body, such as the reproductive and urinary tracts, and can easily spread during sexual activity.
Symptoms
In many cases, gonorrhea can be asymptomatic, especially in women. However, common symptoms of gonorrhea in both men and women may include:
- Pain or burning during urination
- Increased vaginal or penile discharge
- Rectal discomfort or discharge (if transmitted anally)
- Sore throat or swollen glands (if transmitted orally)
It is essential to note that the absence of symptoms does not mean the infection is not present. Asymptomatic individuals can still transmit the infection to others, highlighting the importance of regular STI screenings.
Complications
Left untreated, gonorrhea can lead to severe complications, particularly in women. Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is a serious condition that can cause chronic pelvic pain, ectopic pregnancies, and even infertility. In men, untreated gonorrhea can result in epididymitis, a painful inflammation of the epididymis.
Diagnosis
If you suspect you have been exposed to gonorrhea or experience any symptoms, seeking medical attention is crucial. A healthcare provider can perform various tests, including urine tests and swab samples from affected areas, to confirm the presence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Treatment
Gonorrhea is typically treated with antibiotics, which effectively clear the infection. However, antibiotic-resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae have become a growing concern, making it essential to follow prescribed treatment regimens carefully. Additionally, patients are often advised to inform their sexual partners to ensure they also receive testing and treatment to prevent further transmission.
Prevention
Preventing gonorrhea transmission requires adopting safe sexual practices. Using condoms consistently and correctly during every sexual encounter can significantly reduce the risk of infection. Reducing the number of sexual partners and engaging in open communication about sexual health are also essential preventive measures.
Conclusion
Gonorrhea remains a prevalent STI worldwide, but with early detection and proper treatment, its impact can be mitigated. Regular STI screenings and adopting safe sexual practices are key to preventing the spread of gonorrhea and protecting individual and public health. Raising awareness about the importance of sexual health and promoting responsible behavior are vital in the ongoing battle against this infectious disease.
